树
树是一种被广泛应用的数据结构,例如:
- dom是一种树结构数据
- os中的文件与目录可以视为树
- 家族、族谱
堆、二叉排序树等这些不同的树结构可以解决调度、图像处理、数据库的问题。很多复杂问题也许不是第一眼就能看出是树结构,但是使用树结构解决更加简单与高效。
导言
树的节点包括值、左节点、右结点,因此节点实现:
// 可以实现这样的树结构
// 2
// / \
// 1 3
function Node(value) {
this.value = value;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
const root = new Node(2);
root.left = new Node(1);
root.right = new Node(3)遍历
分为两种: 广度优先遍历(层序遍历) 深度优先遍历
广度优先遍历
逐行从左到右遍历
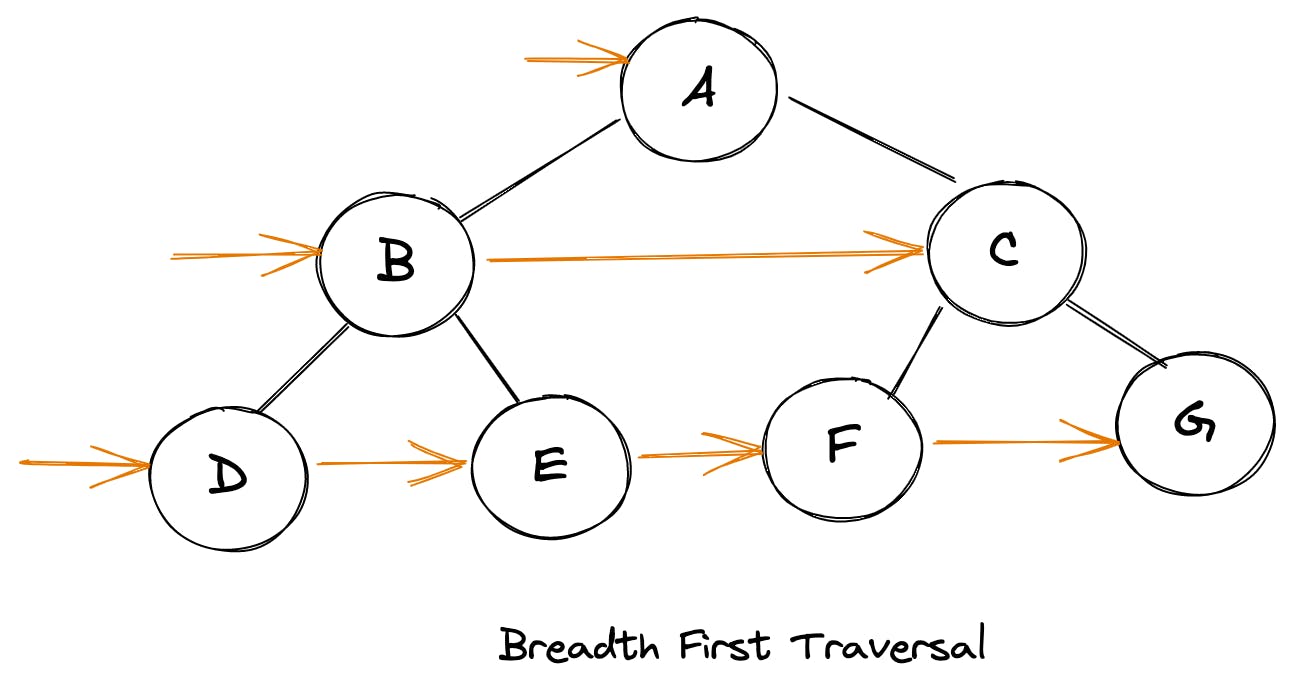
广度优先遍历可以采用队列(先进先出)来实现,大致流程如下:
- 初始化一个带有根节点的队列
- 移出队列的首个结点
- 将移出结点的左子节点与右子结点入队
- 重复二、三步直到队列为空
代码实现:
function walkbfs(root) {
if(!root) return [];
const queue = [root], res = [];
while(queue.length) {
const len = queue.length, level = []; // len 等于当前这一层的节点个数
for(let i = 0; i<len; i++) {
const item = queue.shift();
level.push(item);
if(item.left) queue.push(item.left);
if(item.right) queue.push(item.right);
}
res.push(level);
}
}变种题:
- 二叉树的层平均值 给定一个非空二叉树, 返回一个由每层节点平均值组成的数组 示例 1:
输入:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
输出:[3, 14.5, 11]解释: 第 0 层的平均值是 3 , 第1层是 14.5 , 第2层是 11 。因此返回 [3, 14.5, 11] 。
思路: 将push的值由结点改成平均数
var averageOfLevels = function(root) {
const queue = [root], ans = [];
while(queue.length) {
const len = queue.length; let total = 0;
for(let i=0;i<len;i++) {
const item = queue.shift();
total+=item.val;
if(item.left) queue.push(item.left);
if(item.right) queue.push(item.right);
}
ans.push(total / len);
}
return ans;
};- 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历 给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值的锯齿形层序遍历。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)。
例如: 给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7返回锯齿形层序遍历如下:
[
[3],
[20,9],
[15,7]
]思路:遍历依然是广度遍历,值在需要由右向左时改成unshift
var zigzagLevelOrder = function(root) {
if(!root) return [];
const queue = [root], ans = [];
let index = 0;
while(queue.length) {
const len = queue.length, level = [];
index++;
for(let i=0;i<len;i++) {
const item = queue.shift();
if(index % 2 === 1) {
level.push(item.val)
} else {
level.unshift(item.val)
}
if(item.left) queue.push(item.left);
if(item.right) queue.push(item.right);
}
ans.push(level);
}
return ans;
};- 二叉树的右视图 给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。

输入: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
输出: [1,3,4]思路:遍历依然是那个遍历,只存放每一层的最后一个结点值
var rightSideView = function(root) {
if(!root) return [];
const queue = [root], res = [];
while(queue.length) {
const len = queue.length, temp = [];
for(let i = 0;i<len;i++) {
const item = queue.shift();
if(i === len - 1) {
res.push(item.val);
}
if(item.left) queue.push(item.left);
if(item.right) queue.push(item.right);
}
}
return res;
};- 在每个树行中找最大值
BFS应用二: 最短路径
在一棵树中,一个结点到另一个结点的路径是唯一的,但在图中,结点之间可能有多条路径。其中哪一条路最近为最短路径问题。(先mark)
深度优先遍历
深度优先遍历分为:前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历
前序遍历
根节点 -〉 左节点 -〉 右节点 实现具体类似层序遍历,不过将队列换成栈(先进后出) 迭代实现:
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {
if(!root) return [];
const res = [], stk = [root];
while(stk.length) {
const item = stk.pop();
res.push(item.val);
if(item.right) stk.push(item.right);
if(item.left) stk.push(item.left);
}
return res;
};中序遍历
左节点 -> 根节点 -> 右节点 迭代思路:先找到二叉树的最左节点,然后根节点,最后右节点,所以初步的代码如下:
const cur = root;
while(cur) {
while(cur.left) {
cur = cur.left
}
console.log(cur);
cur = cur.right
}但是上述的代码不能回溯,无法回到父节点,所以需要通过栈记录这些节点
function walkInOrder(root) {
const res = [], stk = [];
let cur = root;
while(cur || stk.length) {
while(cur) {
stk.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
const item = stk.pop();
res.push(item.val);
cur = cur.right;
}
return res;
}后序遍历
左节点 -〉右节点 -〉根节点 实现思路:前序遍历是根-〉左-〉右, 后序遍历是左-〉右-〉根,利用前序遍历改造下顺序,再反转
var postorderTraversal = function(root) {
if(!root) return [];
const res = [], stk =[root];
while(stk.length) {
const node = stk.pop();
res.push(node.val);
if(node.left) stk.push(node.left);
if(node.right) stk.push(node.right);
}
return res.reverse();
};相关阅读
tree-data-structure-in-javascript: https://stackfull.dev/tree-data-structure-in-javascript